Golden Square, Bendigo
B 1873 Robert Mackenzie; reb 1951 Hill, Norman & Beard (o/n V244). 2m, 22spst, 8c, elpn.
Gt: 8.8.8.4.4.2-2/3.2.II.8. Sw: 16.8.8.8.4.2.8.8. Ped: 16.16.8.8.4.
Reb & enl 1990 Vernon Cresswell. 2m, 23spst, 7c, elpn.
Gt: 8.8.8.4.4.2-2/3.2.IV.8. Sw: 8.8.8.4.2.III.8.8. Ped: 16.16.8.8.4.16.

From the 1985 OHTA Conference Handbook:
This imposing building, constructed externally in polychrome brickwork, was designed by Crouch & Wilson, architects, who were also responsible for the original part of the Church of the Immaculate Conception, Hawthorn, the Congregational Churches at Kyneton, Prahran and South Melbourne, and the Methodist Churches at South Yarra and Williamstown. The foundation stone of the Golden Square church was laid on 5 January 1870 and the first section opened on 11 May of that year; the contractors were Johns & Hinley. In 1872 further additions were made and the building completed early in 1873 at a cost of about 4,000 pounds. At the time it was the most imposing church on the Bendigo goldfîelds.
The dimensions of the building are 98ft by 45ft with a total seating capacity of 1,500. The spire rises to a height of 105ft. The interior is notable on account of the large galleries which have cast iron balustrading. Modifications from the original design include the front of the organ loft, the narthex, and the extension of the organ case. Fletcher Jones donated one of the stained glass windows. [1] The organ was built by R. Mackenzie & Co., of Melbourne, at a cost of 520 pounds. It was opened in April 1873 at which time ''the Instrument was not complete, the metal pipes not having arrived from Melbourne. But they are expected in a week or two.'' [2] Mackenzie built numerous organs during the 1870s following his arrival from England to assist in the erection of the Hill & Son organ in the Melbourne Town Hall, which was opened in 1872.
In 1951 the organ was rebuilt by Hill, Norman & Beard, of Clifton Hill, at a cost of 2020 pounds. The action was electrified and a new detached stopkey console provided. The only tonal additions, however, were three stops , derived by extension, on the pedal organ. [3] Consideration is currently being given to a further rebuild/restoration.
This instrument is thought to be the largest example of Robert Mackenzie's work to survive, at least with its original tonal scheme preserved essentially intact.

| Great Open Diapason Claribel Flute Dulciana Principal Flute Twelfth Fifteenth Mixture Trumpet Swell Bourdon Open Diapason Lieblich Gedeckt Keraulphon Principal Piccolo Mixture Horn Oboe Tremulant Pedal Open Diapason Bourdon Octave Flute Octave Flute Trombone |
8 8 8 4 4 2-2/3 2 IV 8 16 8 8 8 4 2 III 8 8 16 16 8 8 4 16 |
gvd. bass orig. II gvd. bass added 1990 A B A B B added 1990 |
Compass: 56/30 (61/30 at console)
8 couplers
16 fixed thumb and toe pistons
2 reversible thumb and toe pistons
balanced mechanical swell pedal
detached stopkey console
electro-pneumatic action [4]

Photos: Trevor Bunning (Aug 1985)
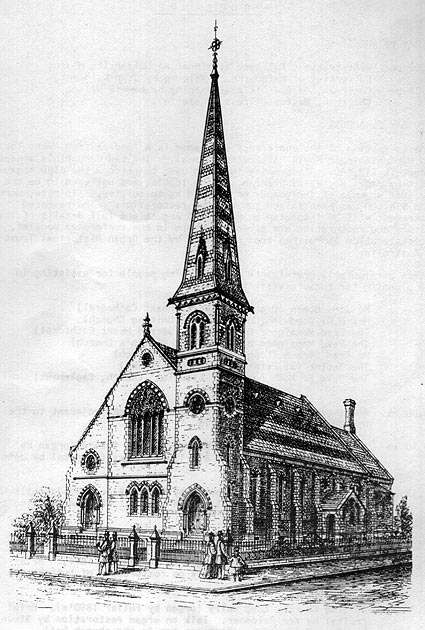
Line drawing from the 1985 Conference Booklet where it was reprinted from the Church History
[1] Historical information derived from George Doenau History of the Golden Square Methodist Church. Bendigo, 1977
[2] The Bendigo Advertiser (undated cutting April 1873)
[3] Hill, Norman & Beard order book, job no. V244, 28 March 1949
[4] Spec. noted John Maidment, March 1966